Let’s take a closer look at what a triple net lease is exactly, how it works and explain why investors gravitate towards this structure.
So, what is it exactly?
Before we dive into any specifics, it’s important to first be aware of the two overarching lease structures in commercial real estate: a gross lease and a net lease. You can think of these on a scale, with absolute gross lease at one end and absolute net lease at the other, with a few hybrid options in between (single, double and triple net leases). Generally, an absolute gross lease requires a high level of responsibility from the investor, while an absolute net lease is the complete opposite.
Now let’s dive a little further into the subtypes. The terms triple net lease and absolute net lease are commonly confused, and though they are very similar in the way almost no responsibilities fall onto the landlord, specific structural costs (i.e. roof repairs) may vary. Additionally, the way the tenants pay the expenses can also set the two apart. In some circumstances with a triple net lease, the landlord may cover the upfront costs on their behalf, and the tenant will provide a reimbursement later.
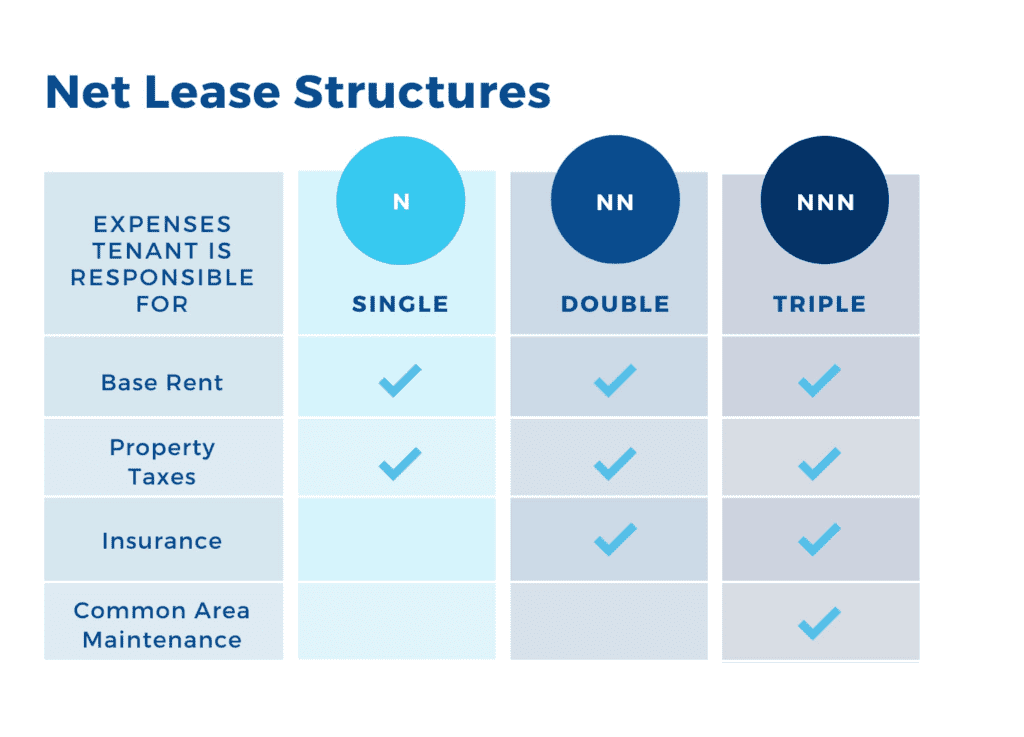
A triple net lease, or NNN lease, is structured so the tenant is responsible for paying the base rent, property taxes, insurance and all maintenance associated with the property, removing the landlord/investor from almost all financial responsibilities.
To compare this to double and single net leases, let’s take a look at the chart below:
Why triple net leases are often the most popular…
It’s evident why triple net leases are attractive from the investor’s standpoint; with little to no expenses required from their end, they can truly enjoy the passive income stream. There are several additional reasons one may choose this structure as well, such as low-maintenance upkeep, consistency and reliability, and the long-term nature of the contract opens the potential for capital appreciation of the property.
And what about from the tenant’s perspective? With almost all operating expenses falling onto their side, it may seem like there’s no benefits. However, with this structure, tenants do usually pay a lower base rent to compensate for the extra costs that may be incurred.
The Takeaway
Understanding the different types of leases can be tricky, even for investors with years of experience. The most important takeaway is to take the time to understand each structure prior to signing any type of lease. Simple labels like “net lease”, for example, can be confusing when the actual terms of the lease do not align, so having knowledge of each structure will make all the difference in your success in the commercial real estate space.





